
With the prevalence of work-from-home in the time of the pandemic, going digital has increasingly become more vital. In compliance with social distancing rules, reinforcement of the electronic signature practice is observed and is predicted to increase by 24.6% within 10 years. More and more people are adapting to this change as digital becomes the new norm.
Though digital is mainstream, there’s still a lot of confusion when it comes to these three terms – digital footprint, digital signature, and electronic signature.

What is a Digital Footprint?
A digital footprint is mostly confused with the other two terms because of the notion that “footprints” leave a mark, therefore concluding that these marks are the signature. Indeed, digital footprint leaves a mark but it does not entail a signature on a document, instead, it involves the trail and traces that the user leaves behind while using the internet.
This mark can be on social media, on a website, forums, or chats and shows the identity of the user by the individual’s activities, communication, and behavior. This footprint can be “passive” or “active,” where passive means that the marks left are unintentional while active means intentionally submitting information online. Examples of a digital footprint are the user’s IP address collected on a website, personal information input on a shopping cart, an email sent, or shared images on social media. This cannot be erased completely but some information can be removed.
What is an Electronic Signature?
Comparable to a handwritten signature, an electronic signature may be a symbol or a written name in its digital format. It is usually attached to, inserted or written over an electronic document with the intention of the user to seal and sign the document for the purpose of the agreement. This is applied using electronic signature software or may also be in the form of an image taken from the actual physical handwritten signature.
An electronic signature is preferred nowadays not only to save time but also to practice social distancing. Instead of holding a meeting to sign documents, users send these digital files online and allows users to sign it with online software. There is no need to print, sign then scan the document. Tools such as Adobe Reader or DeftPDF online can help users sign the document directly and easily.
See also: How to add an Electronic Signature to your Document
Old school users may question the legality of an electronic signature but actually, these signatures are recognized worldwide and are legally binding. The Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act and eIDAS Act was passed in 2000 and in 2016 with the acknowledgment that electronic signatures and records are valid in any transaction, given that the digital document is within standards.
Handwritten signatures are replaced by these electronic signatures when documents are in its virtual form and plenty of people find that this is beneficial in terms of efficiency as it can fasten the transaction. Additionally, e-signatures are also cost-effective because it allows any user to save on ink, paper and courier costs. This is the new way of getting consent from a person, may it be in any eCommerce business or organization.
How can I Send the Documents for Others to Sign?
Traditionally, email is the way to go but if you aren’t sure if the reader knows how to do this and you want to ensure that the document is signed immediately, then using third-party applications like DeftPDF should solve your worries. Here’s how to do it using the online tool:
Step one: Go to DeftPDF.com and select the Fill&Sign tool
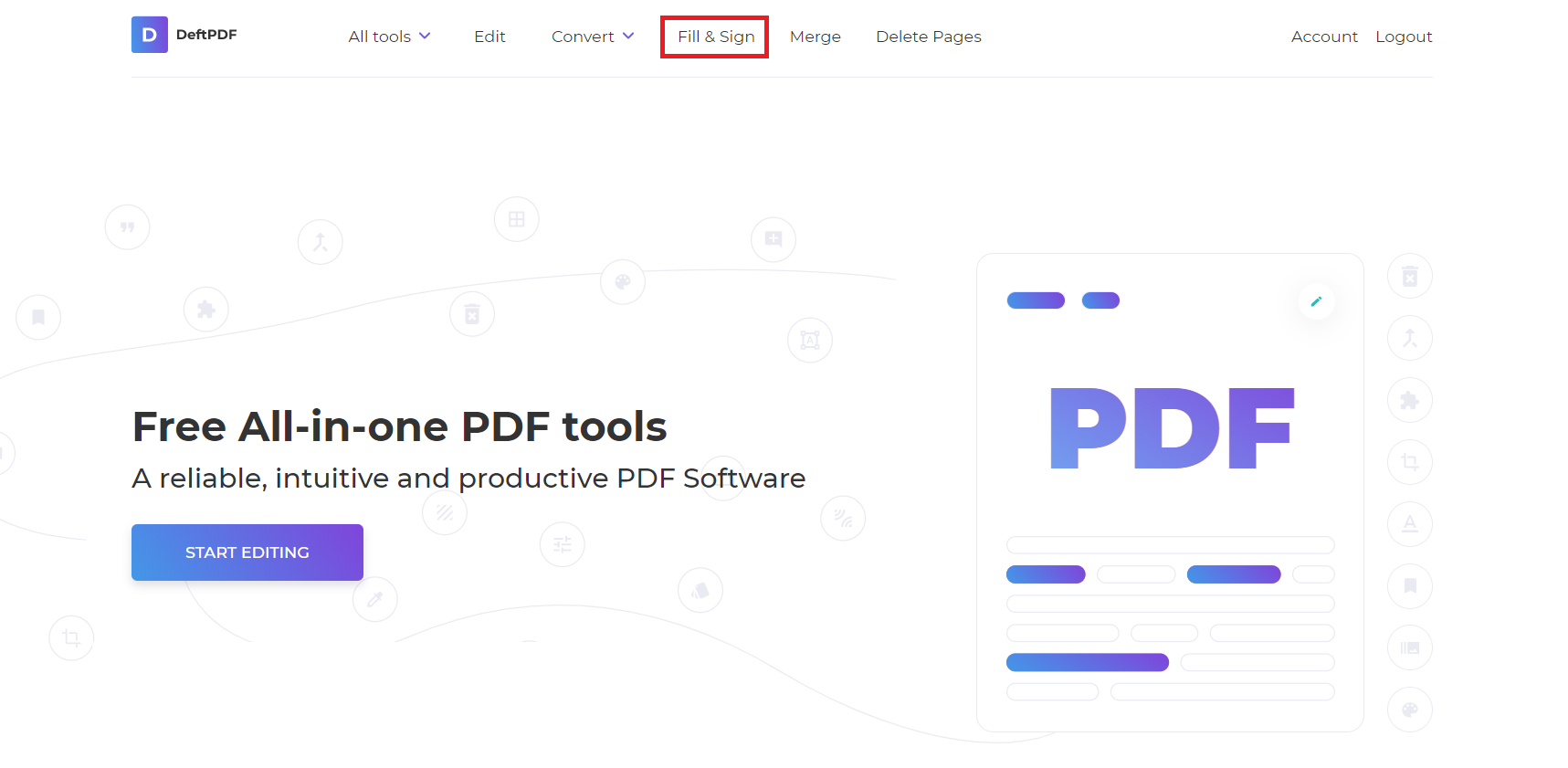
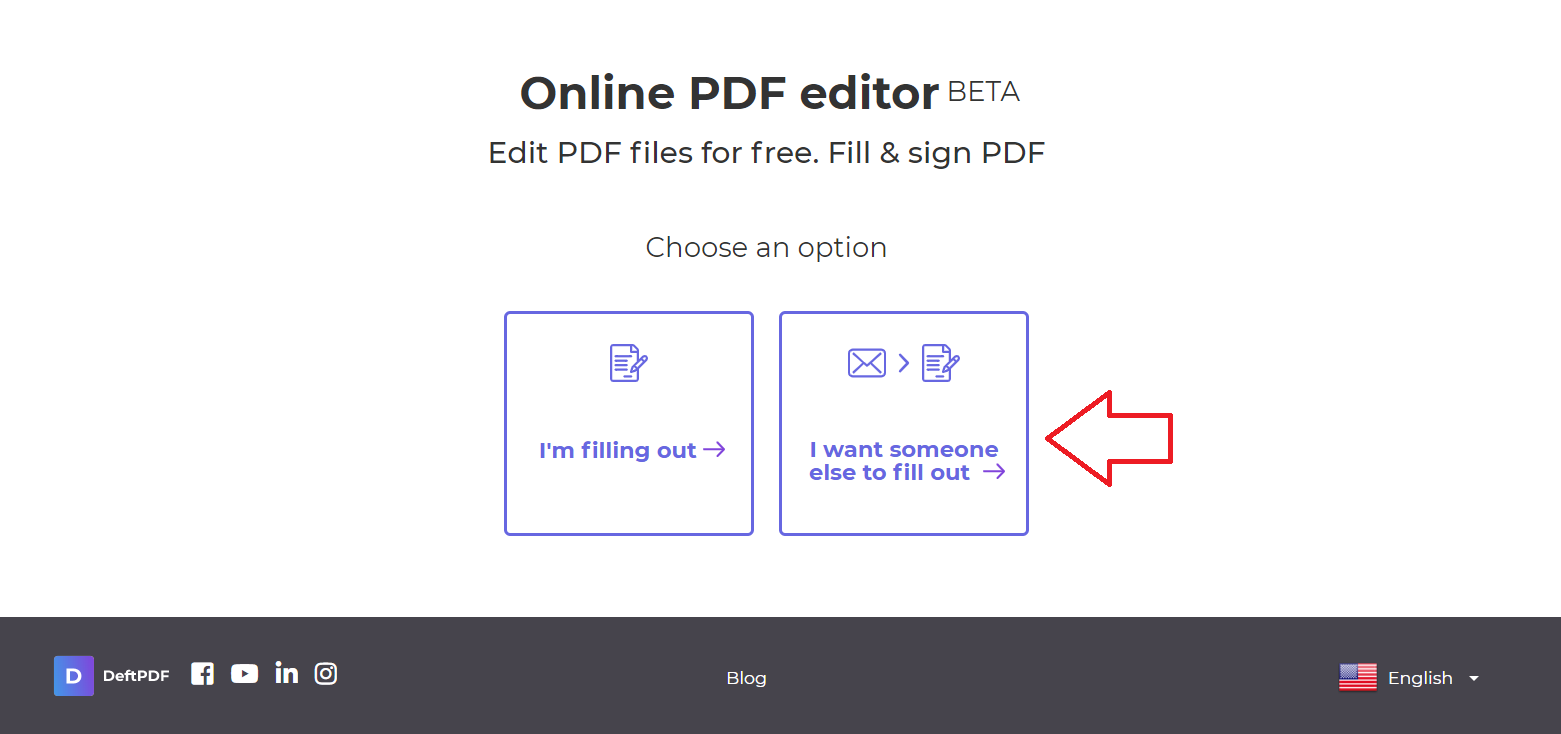
Step two: Upload the file. Once uploaded, two choices will be provided. Choose “I want someone else to fill out”
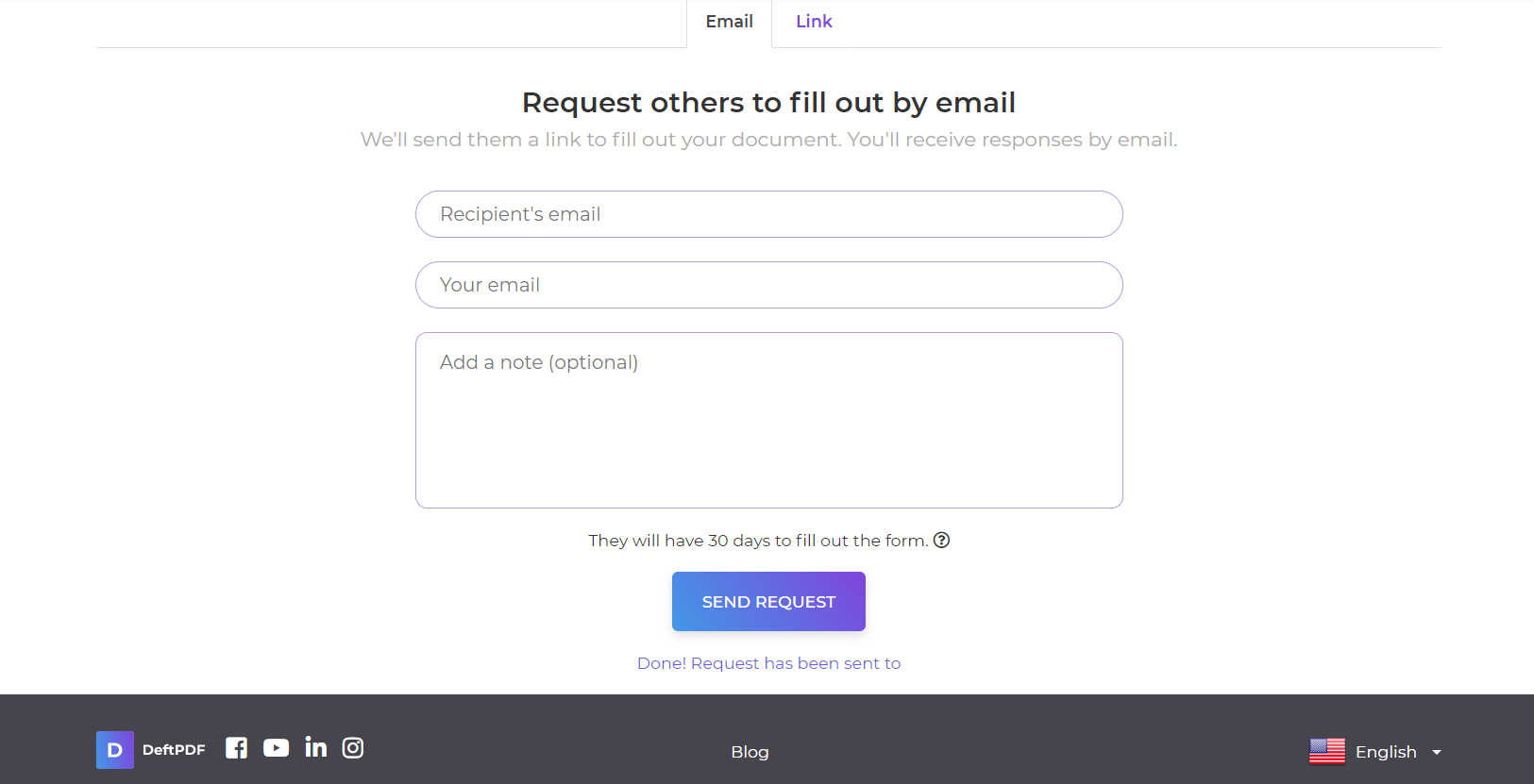
Step three: Input the recipient’s email address and write your message. Then hit “send the request.” This will send them the document with a link. Once they click it, it will redirect them to the document on the fill & sign tool here at DeftPDF so they can sign it right away.
What is a digital signature?
When a user sends over a sensitive document for signature, how does one know that the signature is authentic? This is where digital signatures come in. Basically, a digital signature is the authentication element in the virtual document assuring the receiver that the message came from the sender and was not edited in transit. Digital signatures contain asymmetric cryptography where security is added to the message. With this properly implemented, a digital signature can be recognized as equivalent to the handwritten signature and can also be encrypted using a private key.
When we compare both signature and digital signature, we might get confused with both terms as they are very similar. In a gist, a digital signature is actually a type of electronic signature with additional security levels that include encryption and identity verification using technology to observe legal standards. With a digital signature, certificate-based digital IDs and public key infrastructures are used to back up the validation.
While using basic electronic signatures is sufficient, plenty of users still find that using digital signatures benefits them including security and protection, gaining trust from clients, easy validation, and forgery detection. These are employed in various transactions including financial, distribution, contracts, and software.



